Filing taxes can be a challenging task for anyone, but especially if you’re a student who has multiple sources of income, deductions, and credits. Whether you are a full-time or part-time student, a domestic or international student, or a dependent or independent student, you need to know how to file your taxes correctly and efficiently.
In this article, you’re going to explore the basics of filing taxes as a student, such as what forms you need, what income is taxable, what expenses are deductible, and what benefits you can claim. By the end of this article, you’re going to have a better understanding of how to file taxes if you’re a student.
How to File Taxes If You’re Student
- Learn What Student Taxes Are
- Know Why You Need to File Taxes as a Student
- Determine Filing Status
- Understand What Forms You Need
- Know What Income Is Taxable
- Gather Necessary Documents
- Check Eligibility for Education Credits
- Consider Using Free Filing Options
- Report any Income Accurately
- Explore Available Deductions
- Consider Parental Support and Dependency Status
- Review and File Federal and State Tax Returns
- Understand Tax Deadline
1. Learn What Student Taxes Are

It’s important to explore eligibility for education-related tax credits, like the American Opportunity Credit or the Lifetime Learning Credit, which can reduce your taxable income. Additionally, you need to accurately report any income, including scholarships or grants. You can qualify for deductions, such as the student loan interest deduction. Explore free filing options and understand the impact of parental support on tax filings.
>>>MORE: How to File Taxes If You’re Single
2. Know Why You Need to File Taxes as a Student
To understand how to file taxes if you’re a student, know why it is necessary for you to do so. Filing taxes ensure compliance with tax regulations, helping you avoid legal issues. Secondly, it provides an opportunity to claim valuable tax credits and deductions, such as education credits, that can significantly reduce your tax liability or even result in a tax refund. Additionally, filing taxes establishes a financial record and can be essential for future financial endeavors, like applying for loans or credit.
It’s essential to understand the specific tax implications that relate to being a student, as there are unique credits and deductions tailored to educational expenses. Overall, filing taxes is not only a legal requirement but also a strategic financial move that can lead to your financial benefits as a student.
3. Determine Filing Status

To master how to file taxes as a student, determine your filing status. You’re likely to fall into the “Single” filing status, especially if you are unmarried and not supporting dependents. However, if you are married or have children, you need to consider the “Married Filing Jointly” or “Head of Household” status.
Your filing status affects your tax brackets and the deductions you qualify for, so accurately identifying it is the first step in the tax filing process. Make sure to review the IRS guidelines and choose the status that aligns with your specific circumstances.
4. Understand What Forms You Need
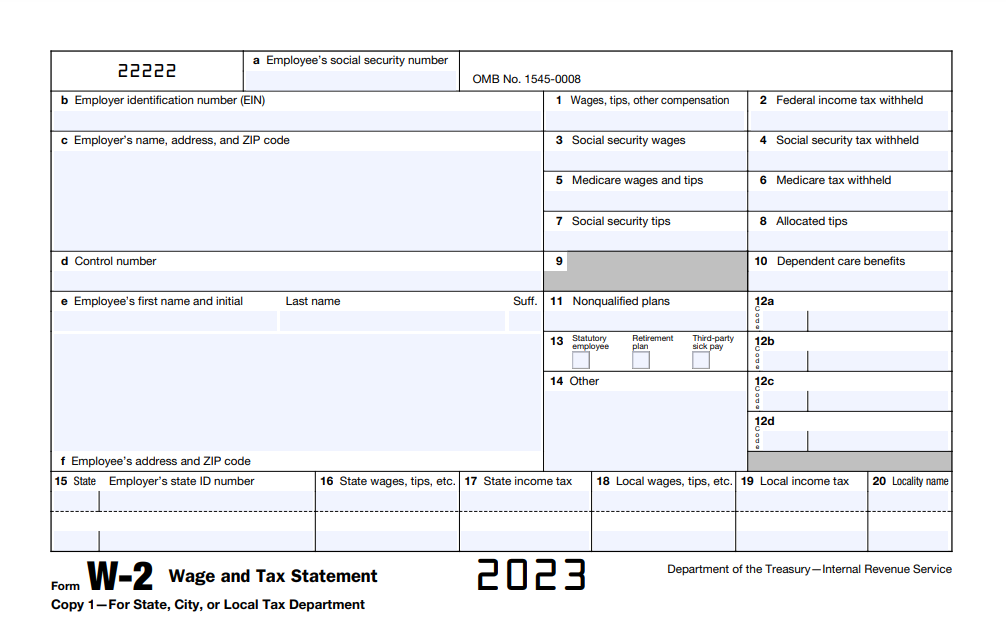
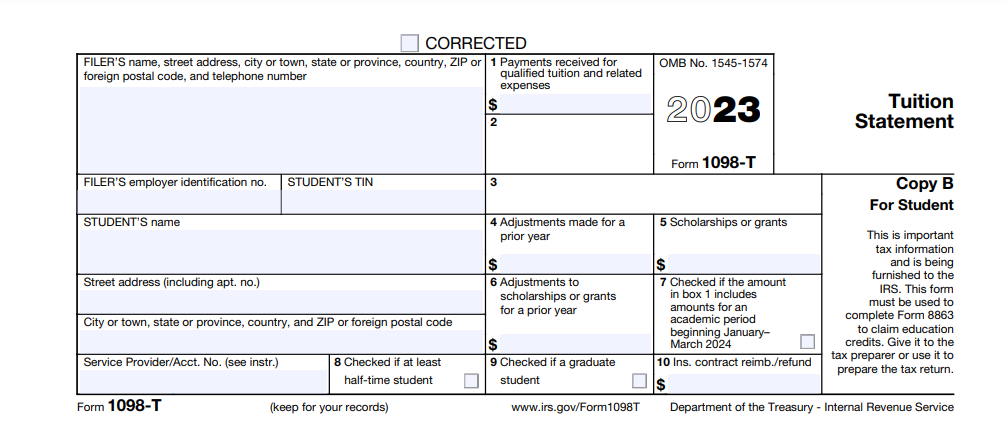
To grasp how to file taxes if you’re a student, understand what forms you need.. Generally, you’re going to receive a W-2 from any employer, detailing your earned income. If you have student loans, a 1098-E form is going to outline the interest you pay. For education expenses, the 1098-T form is key, summarizing your tuition payments.
If you’re working on campus, a 1099-MISC can also be applicable. If you’re on scholarship or grant, you need to keep track of any corresponding paperwork. Additionally, if you’re a dependent, your parents can provide information essential for accurate filing. Familiarizing yourself with these forms ensures you report all necessary details, potentially maximizing deductions and credits available to students.
>>>PRO TIPS: How to File Taxes If You’re Married
5. Know What Income Is Taxable

To familiarize yourself with how to file taxes as a student, know what income is taxable. Generally, wages from part-time jobs, internships, or any other form of employment are taxable. Additionally, scholarships or grants are taxable if they exceed your qualified education expenses. Income from freelance work or self-employment is also subject to taxation.
However, some forms of financial aid, such as loans, gifts, or inheritances, are typically not taxable income. Being aware of the specific types of income that are taxable ensures accurate reporting and helps you take advantage of any available deductions or credits while fulfilling your tax obligations.
6. Gather Necessary Documents
To complete filing your taxes as a student, get her necessary documents. Start by collecting your W-2 form, which reports your income from any employment. Additionally, gather 1098-T forms from your educational institution, detailing tuition payments and possible education credits. If you receive scholarships or grants, have records of those as well.
Keep track of any interest you earn on student loans and any relevant receipts for educational expenses. If you have a part-time job or freelance work, compile income and expense details. Ensuring you have these documents organized streamlines the tax filing process and helps you take advantage of eligible deductions and credits.
7. Check Eligibility for Education Credits

To understand how to file taxes as a student, check eligibility for education credits. Determine if you qualify for either the American Opportunity Credit or the Lifetime Learning Credit. The American Opportunity Credit provides a tax credit for qualified education expenses during the first four years of your higher education, while the Lifetime Learning Credit offers a credit for all years of your post-secondary education.
The American Opportunity Tax Credit (AOTC) is a credit of up to $2,500 per year for the first four years of secondary education. It covers tuition, fees, and course materials. Up to 40% of the credit is refundable, meaning you can get money back even if you owe no tax. However, the credit phases out for higher income levels and is not available for you if you’re a graduate student or dependent.
The Lifetime Learning Credit (LLC) is a credit of up to $2,000 per year for any level of postsecondary education. It covers your tuition, fees, and course materials. The credit is not refundable and phases out for higher income levels. You cannot claim both the AOTC and the LLC for the same student in the same year.
The student loan interest deduction is a deduction of up to $2,500 for interest you pay on qualified student loans. It reduces your taxable income, but not your tax directly. The deduction is available for any level of education and is best for higher income levels. You can claim the deduction even if you do not itemize your deductions.
To claim these credits, ensure that you, your dependent, or a qualifying third party pay eligible education expenses, and the educational institution is an eligible educational institution. Additionally, be mindful of income limits and other eligibility criteria specific to each credit, as they can impact your ability to claim these valuable tax benefits.
>>>GET SMARTER: How to File Taxes If You’re Business Owner
8. Consider Using Free Filing Options
To understand how to file taxes as a student, consider using free filing options. The IRS provides Free File options, partnering with various tax software providers, allowing you to file your federal tax returns for free.
These platforms guide you through the filing process, helping you accurately report income, claim applicable credits, and maximize your refund. It’s essential to review the eligibility criteria for these free filing options to ensure they align with your student status and income level. Utilizing these services can be a cost-effective and efficient way for you to fulfill your tax obligations.
9. Report any Income Accurately

To file taxes as a student, report any income accurately. This includes income from various sources such as part-time employment, internships, or any side gigs. Account for wages, tips, and even scholarships or grants that are taxable.
It’s essential to accurately document all sources of income, ensuring that the figures you report align with the corresponding tax documents, such as W-2s or 1099s. Accuracy in reporting income not only fulfills legal obligations but also helps in determining eligibility for specific credits or deductions that can impact the overall tax liability.
10. Explore Available Deductions
To know how to file taxes as a student, explore available deductions. When exploring available deductions as a student filing taxes, it’s crucial to identify potential deductions that can reduce taxable income. Common deductions include student loan interest, which allows you to subtract the interest you pay on qualifying student loans.
Additionally, tuition and fees deductions can be applicable, enabling you to reduce taxable income by a specific amount for education expenses. Keep an eye on educational-related expenses such as textbooks or necessary supplies that can qualify for deductions. It’s essential to carefully review the IRS guidelines to ensure eligibility for these deductions, maximizing your chances of minimizing taxable income and potentially increasing your tax refund or reducing your tax liability.
11. Consider Parental Support and Dependency Status
To understand how to file taxes as a student, consider parental support and dependency status. If your parents claim you as a dependent on their tax return, it can impact your filing process. Dependent status can affect your eligibility for certain credits and deductions.
Conversely, if nobody claims you as a dependent, you can qualify for additional tax benefits. Ensure clarity on your dependency status by discussing it with your parents and understanding the IRS criteria. This information is vital for accurately completing your tax return and maximizing potential refunds or minimizing any tax liability.
12. Review and File Federal and State Tax Returns
To master how to file taxes as a student, review and file federal and state tax returns. Verify that you claim all eligible deductions and credits, especially those specifically applicable to students, such as the American Opportunity Credit or the Lifetime Learning Credit. Double-check income reporting, including any wages from part-time jobs or internships.
If you earn income in multiple states, be aware of state tax filing requirements. Once you confirm the accuracy of your information, proceed to file your federal tax return through the IRS website or an authorized e-filing service. Additionally, if your state requires income tax filing, use the relevant state tax agency’s website or a trusted e-filing platform to submit your state tax return. Always keep a copy of the returns you file for your records.
13. Understand the Tax Deadline

To familiarize yourself with how to file taxes as a student, understand the tax deadline. The standard deadline for federal tax returns is April 15th, but it can extend to the next business day if it falls on a weekend or holiday. However, if you are a student and receive income from a part-time job or other sources, it’s essential to be aware of deadlines for specific tax forms, such as the W-2 or 1098-T.
Missing these deadlines can result in penalties or missed opportunities for deductions and credits. Additionally, you can qualify for an automatic extension, giving you extra time to file, but it’s important to be mindful of any potential interest on taxes you owe. Stay up-to-date about any changes in deadlines, and consider seeking professional advice if you’re unsure about your filing obligations.
Recap
When filing taxes as a student, it’s crucial to start by understanding what student taxes entail and recognizing the reasons for filing. Determine your filing status and identify the necessary forms, such as W-2 or 1098-T, keeping in mind what income is taxable. Gather essential documents, checking eligibility for education credits and exploring free filing options.
Accuracy is key when reporting income, and it’s beneficial to explore available deductions while considering factors like parental support and dependency status. Finally, review and file both federal and state tax returns, keeping a keen eye on the tax deadline to avoid penalties or missed opportunities. This comprehensive approach ensures a thorough and efficient filing process for students.
This post is to be used for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, business, or tax advice. Each person should consult his or her own attorney, business advisor, or tax advisor with respect to matters referenced in this post. . For comprehensive tax, legal or financial advice, always contact a qualified professional in your area. S’witty Kiwi assumes no liability for actions taken in reliance upon the information contained herein.








No Comment! Be the first one.