Introduction
Schedule F, Profit or Loss from Farming, is a tax form you need as a farmer to report income and expenses related to agricultural activities. You use this form to detail revenues from the sale of your crops, livestock, and other products you produce on the farm.
You also report expenses such as seeds, feed, equipment maintenance, and operational costs necessary for farming operations. This form enables you to calculate your net profit or loss from farming activities, which ultimately impacts your tax obligations. It’s crucial you accurately document all income and expenses, ensuring compliance with IRS regulations.
While preparing this schedule, you need to be meticulous in categorizing your earnings and expenditures, as any inaccuracies can affect your tax liability. This article will help you understand Schedule F because it remains an essential document for you as a farmer, providing a comprehensive overview of your financial standing within the agricultural sector.
What Is Schedule F: Profit or Loss from Farming?
1. Farm Financials Overview
2. Income Reporting
3. Expense Deductions
4. Farming Operations
5. Net Profit Calculation
6. Tax Implications
7. Required Documents
8. How to File
Recap
1. Farm Financials Overview
Schedule F offers you a comprehensive glimpse into your farm’s financial landscape. Within this schedule, you’ll find where to input a detailed breakdown of your farm’s income sources and expenses. You report various earnings, such as income from livestock sales, crops sold, or any other products you harvest or raise on your farm.
Conversely, you also document essential expenses, encompassing everything from seed purchases to equipment maintenance, feed costs, and operational expenses directly tied to your farming activities. This form acts as a financial snapshot, illustrating your farm’s economic health by calculating the net profit or loss you derive from your agricultural endeavors.
It’s a crucial tool, enabling you to evaluate the financial performance of your farming operations over a specific period. Make sure you utilize Schedule F accurately as it ensures compliance with IRS guidelines, presenting a clear and organized overview of your farm’s financial standing. Don’t forget to keep meticulous records so you can provide an accurate portrayal of your farm’s finances.
>>>MORE: What Are Tax Schedules?
2. Income Reporting
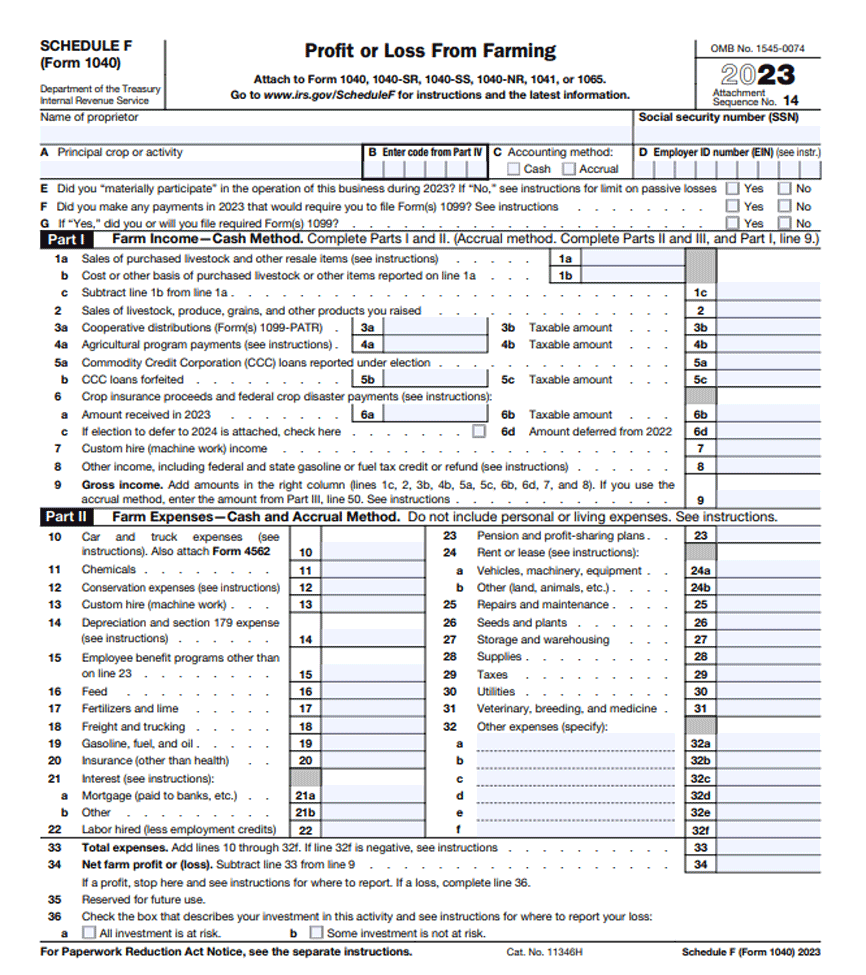
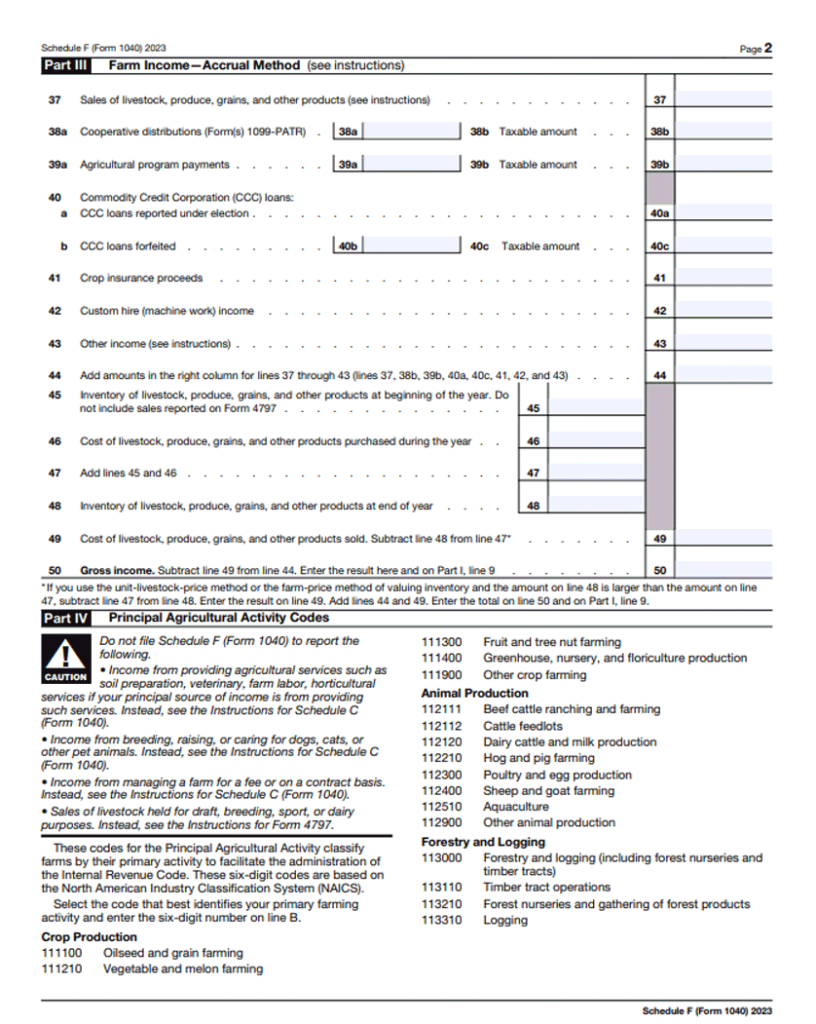
Income reporting within Schedule F involves documenting all revenue you generate through farming activities. You, as a farmer, must detail every source of income your farm generates, including sales of crops, livestock, products like honey or timber, and government subsidies you receive for agricultural purposes.
It’s essential you accurately record these earnings, providing a clear breakdown of the income sources for your farming operations. This section captures both cash and non-cash income, ensuring a comprehensive overview of all financial inflows related to your farm.
Remember, proper categorization of income sources is critical, as it directly impacts your tax liability and contributes to a precise representation of your farm’s economic activities. Stay updated with IRS guidelines to ensure adherence to current reporting standards for agricultural income.
3. Expense Deductions
Expense deductions within Schedule F entail detailing the various costs you incur during your farming operations. As a farmer, you are allowed to deduct legitimate expenses essential for running your farm.
These deductions include expenses related to seeds, fertilizers, feed, livestock care, equipment maintenance, utilities, rent for land or buildings you use for farming, and even insurance premiums. It’s crucial you keep thorough records of these expenses, organizing them accurately to substantiate the deductions you claim.
By accurately reporting these expenses, you ensure a fair representation of the actual costs involved in maintaining your farm. However, it’s important you note that not all expenses are eligible for deductions, so make sure you understand the IRS guidelines regarding deductible farming expenses.
Being updated with current IRS regulations helps you maximize legitimate deductions while staying compliant with tax laws governing farming operations.
4. Farming Operations
Farming operations encompass all activities you undergo to manage and run your farm. You, as a farmer, undertake a multitude of tasks essential to cultivate crops, raise livestock, or produce goods. These operations cover a broad spectrum: planting and tending crops, animal care, irrigation, pest control, harvesting, and more.
Every task, from soil preparation to post-harvest handling, falls under the umbrella of farming operations. It’s crucial you manage these activities efficiently to ensure optimal productivity and yield. Your dedication and expertise in handling these operations directly impact the success and profitability of your farm.
By understanding the intricacies of farming operations, you can accurately depict the financial aspects of your agricultural activities on Schedule F, ensuring compliance with IRS regulations and a precise representation of your farm’s profitability or losses.
Additionally, factors like weather conditions, market demands, and technological advancements influence the dynamics of farming operations. Stay informed about modern agricultural practices and adapt to changes to ensure your farming operations remain effective and sustainable in the long run.
>>>PRO TIPS: The Self-Employment Tax
5. Net Profit Calculation
Calculating your net profit on Schedule F involves determining the financial outcome of your farming endeavors. You subtract your total allowable expenses from your gross farm income. This process results in the net profit or loss from your farming activities.
Make sure you accurately account for all income and expenses to derive an exact net profit figure. Your gross income includes proceeds from sales of crops, livestock, and any other farm-related income. Deductible expenses cover a wide range, such as operating costs, maintenance, supplies, and other essential expenditures directly linked to your farming operations.
By subtracting these expenses from your gross income, you obtain your net profit, a crucial figure that indicates the financial health of your farm. Ensure you calculate and report your net profit accurately because it is vital not only for tax purposes but also for evaluating the success and sustainability of your farming business.
6. Tax Implications
Take note of the tax implications related to the net profit or loss you report on Schedule F because it is vital for managing your farm’s financial responsibilities. As a farmer, you must recognize that this net profit or loss directly influences your tax liability.
The amount you owe in taxes or the deductions you can claim is directly tied to the accuracy of the figure you report. A higher net profit could mean a higher tax obligation, while a loss might result in tax benefits or reduce the taxes you owe.
It’s crucial you ensure meticulous accuracy when calculating and reporting this figure to avoid potential IRS issues. Stay updated with current tax laws and regulations as it often impacts the deductions, credits, or exemptions available to farmers. You may seek guidance from a tax professional who can provide invaluable assistance in navigating these complexities.
>>>GET SMARTER: Schedule B (Form 1040A or 1040): What It Is, How to File It
7. Required Documents
To accurately file Schedule F, you need the following documents:
- Income Records: These encompass sales receipts, crop sales records, livestock sales, and any other income you generate from farming activities.
- Expense Receipts: Keep records of all expenses related to farming, including receipts for seeds, feed, equipment purchases, maintenance, utilities, and any other costs directly linked to your farm operations.
- Inventory Records: Maintain detailed inventory records for crops, livestock, or any other products you use or sold during the tax year. This includes opening and closing inventory values.
- Asset Records: Document details of farm assets like equipment, machinery, and buildings you use for farming operations. Record depreciation and any disposals or purchases during the year.
- Financial Statements: Keep copies of balance sheets, profit and loss statements, and any other financial documents reflecting your farm’s financial position and performance. These records support the income and expenses you report on Schedule F.
8. How to File
Here is a detailed step by step guide on how you can file Schedule F:
- Gather Records: Collect all income and expense records, inventory details, asset documents, and financial statements related to your farm activities.
- Download Form: Obtain Schedule F from the IRS website or acquire it from a tax preparation software if you’re filing electronically.
- Enter Information: Transfer your farm’s income, expenses, inventory values, and asset details accurately onto Schedule F.
- Calculate Totals: Sum up all income and expenses to determine the net profit or loss for your farming activities during the tax year.
- Fill Other Sections: Complete other necessary sections of Schedule F, such as information regarding farm rental income or expenses.
- Attach to Tax Return: Include your completed Schedule F when filing your annual income tax return, whether you’re filing electronically or by mail.
- Keep Records: Retain a copy of your filled Schedule F along with all supporting documents for at least three years in case of IRS inquiries or audits.
Recap
Schedule F, Profit or Loss from Farming, is an IRS form you use as a farmer to document your farm income, deductible expenses, and calculate your net profit or loss. This form, when accurately completed, determines your tax obligations and presents a comprehensive financial snapshot of your farming activities.








No Comment! Be the first one.