Introduction
Navigating through IRS tax forms can be a daunting task, but understanding its purpose is crucial for managing your taxes. These forms serve as the foundation for accurately reporting your income, deductions, and credits to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
You’ll encounter various forms depending on your financial circumstances, each designed for specific reporting needs. For instance, the W-2 form details your earned income, while the 1099 series covers income from various sources like freelance work or investments.
This guide will demystify the common IRS forms, empowering you to navigate tax season confidently and accurately report your financial information. It’s crucial you understand these forms to ensure compliance with tax laws and maximize eligible deductions or credits.
A Guide to Commonly-Used IRS Tax Forms:
1. W-2: Earned Income
2. 1099 Series: Various Income
3. 1040: Individual Return
4. 1040-A: Simplified Return
5. 1040-EZ: Basic Return
6. 8962: Premium Tax Credit
7. 8862: Earned Income Credit
8. 2441: Child and Dependent Care Expenses
9. Schedule A: Itemized Deductions
10. Schedule C: Business Income
Recap
1. W-2: Earned Income
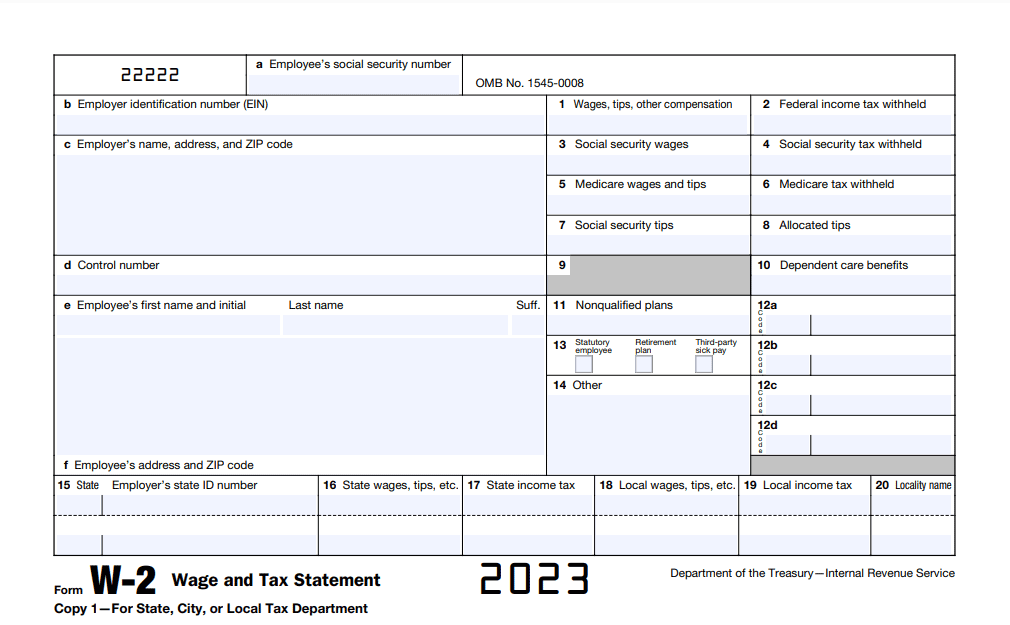
The W-2 form is critical when reporting your earned income to the IRS. If you work as an employee, your employer provides this form, summarizing your annual earnings and the taxes withheld.
It’s vital you verify the details on your W-2, ensuring accuracy in reporting your income on your tax return. This form delineates various income sources, including wages, tips, and other compensations you received.
You’ll find key figures like Social Security and Medicare taxes withheld, crucial for accurately calculating your tax liability. Remember, your W-2 is essential for filing your taxes accurately, as it reflects your earned income throughout the year. Always keep it handy and cross-check the information while preparing your tax return.
>>>MORE: Tax Forms for Reporting Unemployment
2. 1099 Series: Various Income
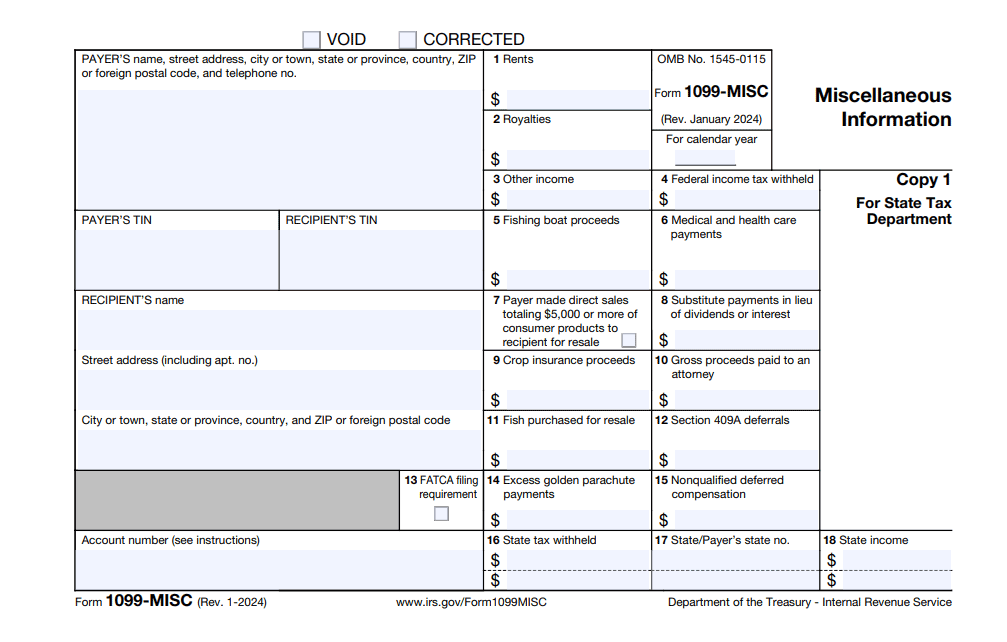
The 1099 series consists of forms that report various types of income beyond traditional employment wages. When you receive income not associated with a regular job, these forms come into play.
For instance, if you freelance, earn interest, receive dividends, or work as an independent contractor, you’re likely to get a 1099 form. Each form within this series corresponds to a different type of income. For example, the 1099-INT covers interest you earn, while the 1099-DIV reports your dividends.
It’s essential you gather all 1099 forms you received and accurately report each income source on your tax return. Be diligent in ensuring you have all the necessary forms in hand, as it accounts for your diverse income streams beyond your standard paycheck.
3. 1040: Individual Return
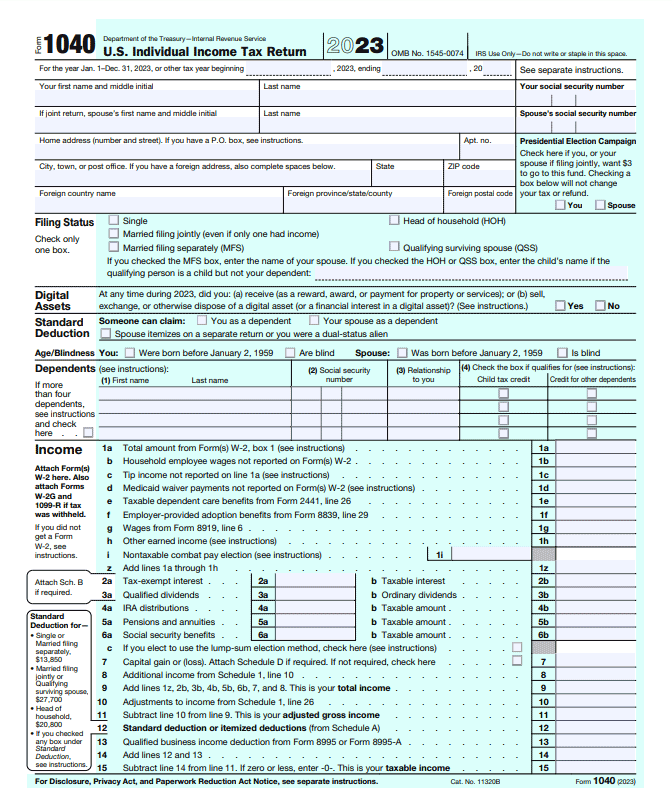
The cornerstone of your individual tax return is IRS Form 1040. When you file your taxes, this form serves as your primary document, summarizing your income, deductions, and tax credits. It allows you to report various sources of income, such as wages, interest, dividends, and retirement distributions.
Additionally, you can claim deductions like mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and education expenses. The 1040 form is versatile, offering you different versions based on your tax situation.
For instance, if you have a straightforward return, the 1040-EZ might be suitable, while the 1040-A allows for more deductions than the EZ version. Always ensure accuracy and completeness when filling out this form, as it forms the basis of your tax reporting to the IRS.
4. 1040-A: Simplified Return
Form 1040-A, also known as the “Simplified Return,” streamlines your tax filing process. It’s designed for you if you’re a taxpayer with moderate income and fewer deductions. This form offers you a middle ground between the basic 1040-EZ and the more complex 1040.
With the 1040-A, you can report your income from various sources, claim tax credits, and include specific deductions, such as educator expenses, IRA contributions, and student loan interest.
This form simplifies your tax return by allowing you to take advantage of certain deductions without navigating the complexities of the full 1040 form. Always verify your eligibility and ensure accuracy while using the 1040-A. It helps you streamline your filing while ensuring compliance with IRS regulations.
>>>PRO TIPS: Income Tax Forms: Everything You Need to Know
5. 1040-EZ: Basic Return
IRS Form 1040EZ, or Income Tax Return for Single and Joint Filers with No Dependents, was the shortened version of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) Form 1040. Discontinued as of the year 2018, but still being used by a few taxpayers with specific tax filing situations pertaining to tax years pre-2018, this form was for taxpayers with basic tax situations and offered a quick and easy way to file income taxes.
The form was discontinued as of the 2018 tax year in favor of the redesigned Form 1040. If you have a single filing status, no dependents, and minimal interest income, Form 1040-EZ might be for you. This form was known as the “Basic Return” and it is a simplified option for straightforward tax situations.
It allowed you to report your wages, salaries, and a few types of income like unemployment compensation or interest. With the 1040-EZ, you didn’t need to dive into itemized deductions—instead, you claimed a standard deduction to reduce your taxable income.
This form streamlined your tax filing process, making it quick and straightforward. If you had tax situations pertaining to pre-2018 and need to use Form 1040-EZ, just ensure you meet the eligibility criteria before using it. Form 1040-EZ is ideal for those with uncomplicated tax situations, providing you with a hassle-free way to fulfill your tax obligations. Always double-check its suitability based on your financial scenario.
6. 8962: Premium Tax Credit
You need IRS Form 8962, the “Premium Tax Credit,” to reconcile the advance payments of the health insurance premium tax credit with the actual credit you’re eligible for.
If you obtained health coverage through the Health Insurance Marketplace and you received advance payments to reduce your monthly premiums, this form comes into play. It ensures that the amount you received aligns with the credit you qualify for based on your income and family size.
When you file your tax return, you’ll use Form 8962 to calculate the correct premium tax credit. Be accurate when filling out this form as any discrepancies could affect the credit you’re entitled to, impacting your tax liability or refund. Always keep track of changes in healthcare laws that might influence this credit.
7. 8862: Earned Income Credit
Form 8862, the “Earned Income Credit” (EIC), ensures you correctly claim this valuable credit if it was previously denied or reduced. If the IRS denied your EIC in a prior tax year, this form allows you to requalify by addressing the reasons for the denial.
It’s essential you understand why you were ineligible previously and rectify those issues to claim the EIC in the present or future years. By completing Form 8862, you provide additional information or address discrepancies, demonstrating your eligibility for this credit.
Accurately filling out this form is crucial as it reinstates your eligibility for the EIC, which can significantly reduce your tax liability or result in a refund. Make sure you stay informed about any updates or changes related to the EIC to ensure accurate eligibility and claiming processes.
>>>GET SMARTER: Business Tax Cheat Sheet on IRS Forms, Schedules and Resources
8. 2441: Child and Dependent Care Expenses
To claim tax credit for qualified expenses you paid to care for your child or dependent while you work or look for work, use IRS Form 2441. This form focuses on “Child and Dependent Care Expenses.”
If you paid for childcare or certain care services for a dependent, such as an elderly parent, this form allows you to claim a credit for these expenses. It’s essential you keep accurate records and receipts for these costs to support your claim.
Form 2441 allows you to calculate the credit amount based on your eligible expenses, potentially reducing your tax bill. Be attentive to the specific criteria for qualifying expenses and ensure your child or dependent meets the IRS guidelines. You should also take note of any changes to these guidelines to ensure accurate and eligible claims for this credit.
9. Schedule A: Itemized Deductions
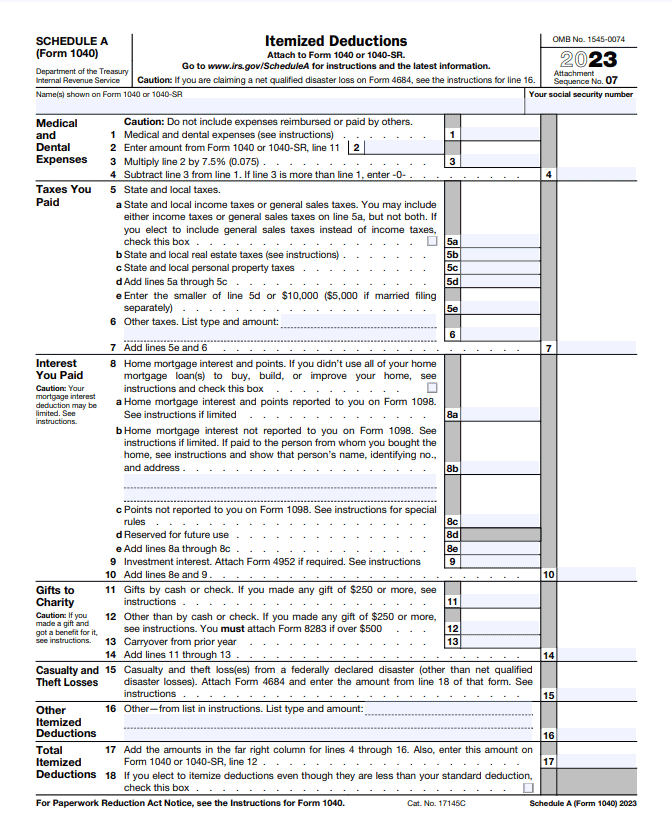
Schedule A, known as “Itemized Deductions,” allows you to claim specific expenses to lower your taxable income. Instead of taking the standard deduction, you can itemize various qualifying expenses, potentially reducing your tax liability.
This form covers various deductions, such as medical and dental expenses, state and local taxes, mortgage interest, charitable donations, and certain job-related costs. By using Schedule A, you have the opportunity to deduct significant expenses, but it’s essential you ensure these deductions meet IRS requirements.
Keep meticulous records and receipts for all itemized deductions to support your claims during an IRS audit. Be informed about eligible deductions and changes to tax laws so you can maximize your deductions while accurately following IRS guidelines.
10. Schedule C: Business Income
Use Schedule C, designated for “Business Income,” to report profits or losses from your business. If you’re self-employed or a sole proprietor, this form allows you to detail your business income and deductible expenses.
Make sure you report your gross income, subtract eligible business expenses, and arrive at your net profit or loss. It’s vital you accurately document all business-related income and expenses throughout the year to ensure precise reporting on this form.
Whether you’re running a small business or engaging in freelance work, Schedule C plays a pivotal role in determining your taxable income. Check the IRS guidelines for deductible business expenses to ensure compliance and maximize your eligible deductions.
Recap
W-2, 1099 series, 1040 variations, and others are commonly-used IRS tax forms that are essential for accurately reporting your income and deductions. These forms help you navigate tax filing, claim credits, and ensure compliance with IRS regulations.








No Comment! Be the first one.